Intramembranous Ossification, Plos One Role Of Matrix Metalloproteinase 13 In Both Endochondral And Intramembranous Ossification During Skeletal Regeneration
Intramembranous ossification Indeed recently has been hunted by users around us, maybe one of you. People now are accustomed to using the net in gadgets to view image and video information for inspiration, and according to the title of this post I will talk about about Intramembranous Ossification.
- Connective Tissue Lec 8 Docx د انعام Muhadharaty
- Intramembranous Bone Formation Process Intramembranous Ossification Download Scientific Diagram
- Intramembranous Ossification Histology Flashcards Draw It To Know It
- Intramembranous Ossification
- Formation Of Bone
- Intramembranous Ossification Wikipedia
Find, Read, And Discover Intramembranous Ossification, Such Us:
- Bone Development And Growth Intechopen
- Soluble Vegfr1 Reverses Bmp2 Inhibition Of Intramembranous Ossification During Healing Of Cortical Bone Defects Hu 2017 Journal Of Orthopaedic Research Wiley Online Library
- Intramembranous Ossification Diagram Quizlet
- Physiology Knowosteoporosis
- Bone Growth And Development Biology For Majors Ii
If you are searching for Hinge Joints Are Monoaxial you've reached the perfect place. We ve got 104 graphics about hinge joints are monoaxial including images, photos, photographs, backgrounds, and more. In these page, we also provide variety of images out there. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, black and white, transparent, etc.

Anatomy Gross Anatomy Physiology Cells Cytology Cell Physiology Organelles Tissues Histology Organs Regional Anatomy Organ Hinge Joints Are Monoaxial
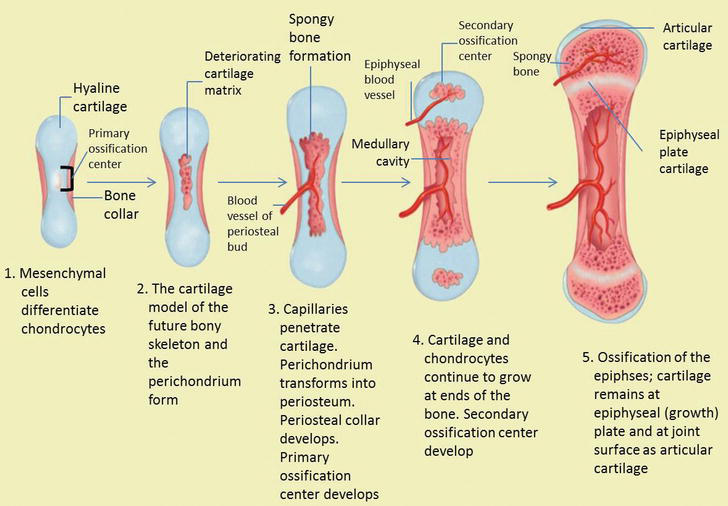
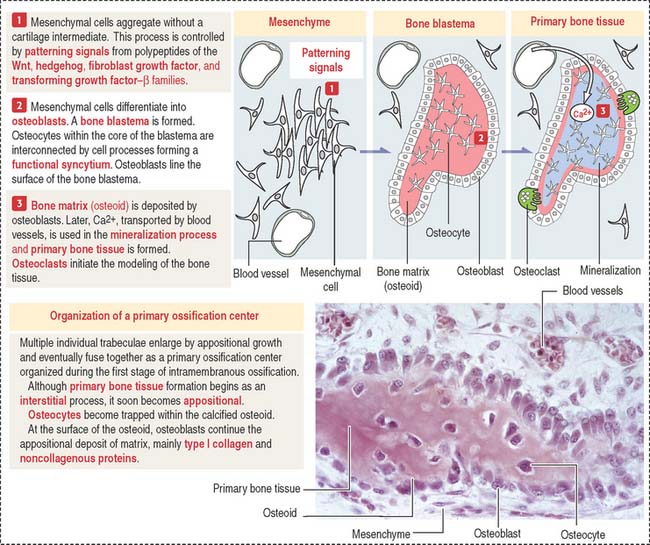
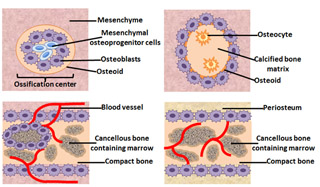
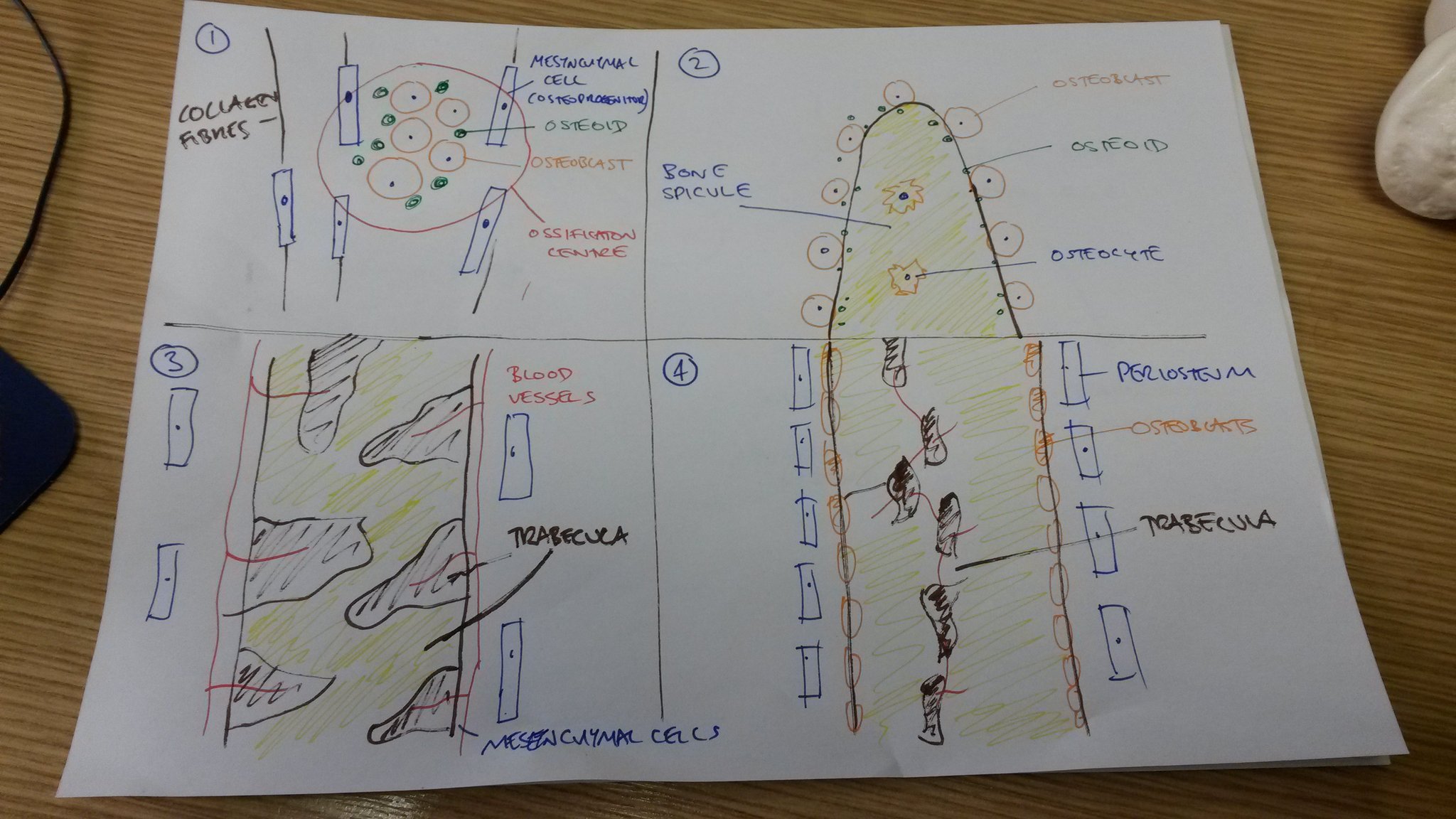
Intramembranous ossification is a type of bone ossification where the bone tissue is created directly over the mesenchymal tissue and not on cartilage as in endochondral ossification.
Hinge joints are monoaxial. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal healthy bone tissue. There are four major steps that occur throughout this process that i will highlight here and elaborate more on in the video. Intramembranous ossification is also an essential process during the natural healing of bone fractures and the rudimentary formation of bones of the head.
These intramembranous bones are formed by the evolution of mesenchyme cells to form osteoprogenitor cells which become osteoblasts. Intramembranous ossification is a process which leads to the formation of jaw bones collar bones or clavicles. Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue while endochondral ossification.
Ossification osi fi kashun formation of or conversion into bone or a bony substance. Furthermore endochondral ossification is involved in the formation of long bones while intramembranous ossification is. The main difference between endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification is that the endochondral ossification is the method of forming a bone through a cartilage intermediate while the intramembranous ossification directly forms the bone on the mesenchyme.
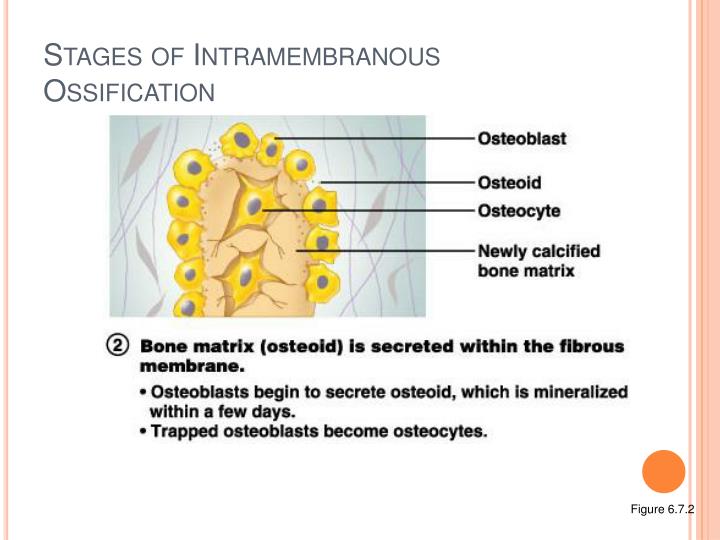
What is intramembranous ossification. In this process the mesenchyme first differentiates in to osteoblasts boneforming cell which then begins to deposits osteoid unmineralized matrix. The osteoblasts secrete osteoid directly onto the.
Intramembranous ossification is the direct deposition of bone on thin layers of connective tissue and is characteristic of the bones on the top of the skull. Intramembranous ossification describes the process of ossification from mesenchymal cells stem cells without a cartilaginous template and is involved in the healing process of fractures. The stages of intramembranous ossification osteogenesis are as follows.
Intramembranous ossification is a type of bone ossification process that doesnt involve a cartilage precursor but the bone tissue is directly formed over the mesenchymal tissue. Endochondral ossification ossification that occurs in and replaces cartilage. The word mesenchyme is a more or less a term used to describe embryonic connective tissue.
Ossification or osteogenesis in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblastsit is synonymous with bone tissue formation. Mesenchymal cells differentiate into osteoblasts. Intramembranous ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the gnathostome excluding chondrichthyans such as sharks skeletal system by which rudimentary bone tissue is created.
Is the process of bone formation in which the mesenchyme differentiated directly into the bone example is the flat bones of the skull.
More From Hinge Joints Are Monoaxial
- Ball And Socket Joints Function
- Hinge Joint Jig
- A Hinge Joint Permits
- Hinge Joint Medical Terminology
- Hinge Joints Permit Movement In Only One Plane True False
Incoming Search Terms:
- Development And Growth Of The Bones Docx Docsity Hinge Joints Permit Movement In Only One Plane True False,
- Connective Tissue Lec 8 Docx د انعام Muhadharaty Hinge Joints Permit Movement In Only One Plane True False,
- Osteogenesis Basicmedical Key Hinge Joints Permit Movement In Only One Plane True False,
- Solved 9 Bones Develop In Two Ways Intramembranous Ossi Chegg Com Hinge Joints Permit Movement In Only One Plane True False,
- Intramembranous Ossification Youtube Hinge Joints Permit Movement In Only One Plane True False,
- Intramembranous Ossification 978 613 3 82381 5 613382381x 9786133823815 Hinge Joints Permit Movement In Only One Plane True False,