Intramembranous Ossification Vs Endochondral Ossification Bones, Endochondral Ossification An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Intramembranous ossification vs endochondral ossification bones Indeed lately has been sought by users around us, maybe one of you. People now are accustomed to using the net in gadgets to view image and video information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about Intramembranous Ossification Vs Endochondral Ossification Bones.
- Development Of Skull Development Of Human Skeletal System
- Bone Development During Fetal Development Ppt Video Online Download
- Bone
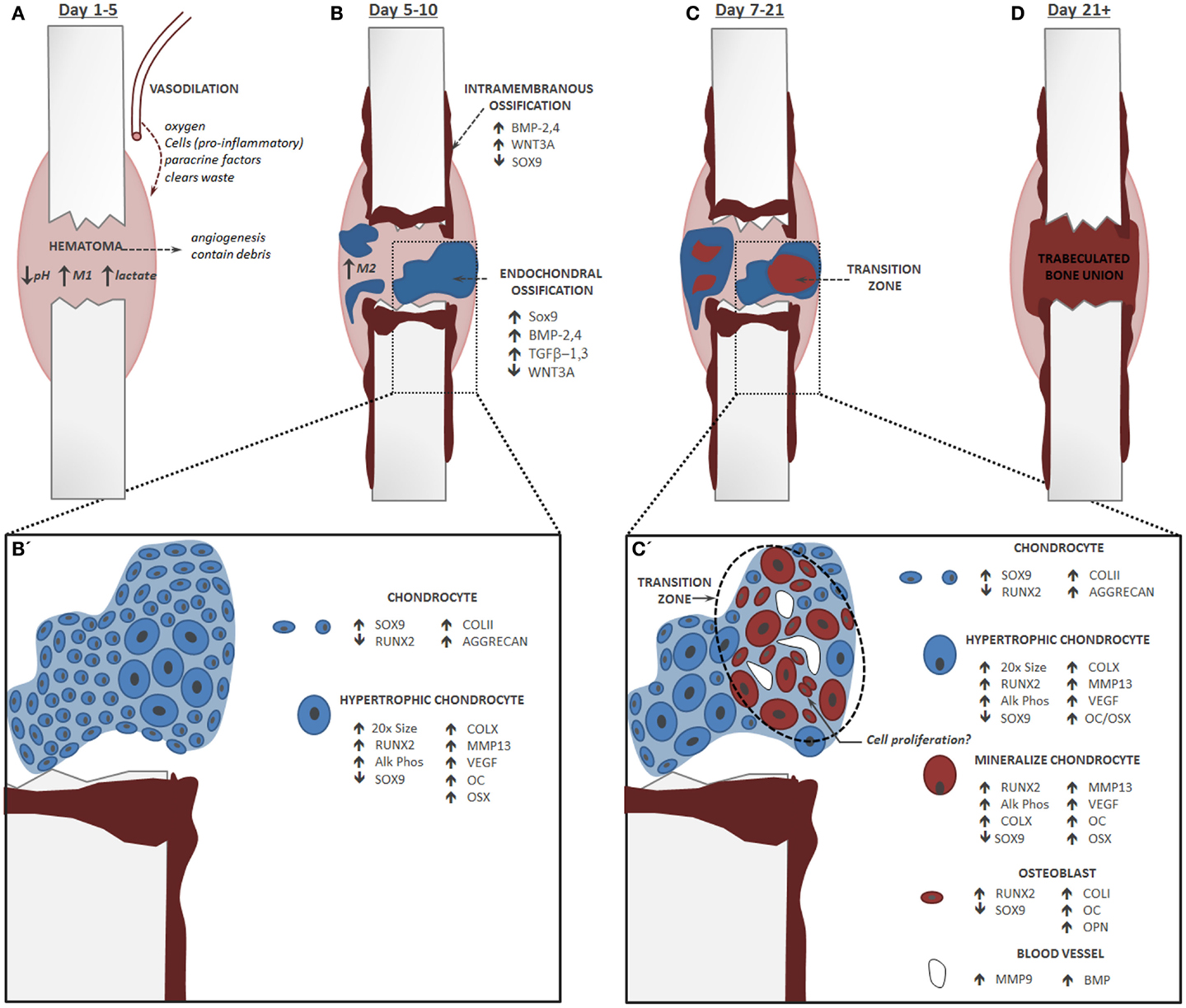
- The Role Of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor In Ossification International Journal Of Oral Science
- 1
- Endochondral Ossification Chap 6 Diagram Quizlet
Find, Read, And Discover Intramembranous Ossification Vs Endochondral Ossification Bones, Such Us:
- Growth Development Endochondral Vs Intramembranous Ossification Nbde Adat Youtube
- Revision Notes Human Anatomy And Physiology Comparison Of Intramembranous And Studocu
- Osteogenesis Basicmedical Key
- Engineering Of A Functional Bone Organ Through Endochondral Ossification Pnas
- Bone Growth Development Factors Endochondral Ossification Biology Class Video Study Com
If you are searching for Osteoblast Definition Biology you've come to the right location. We have 104 images about osteoblast definition biology adding pictures, pictures, photos, wallpapers, and more. In these page, we also have variety of images available. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, black and white, translucent, etc.

Intramembranous Ossification Vs Endochondral Ossification Google Search Human Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Osteoblast Definition Biology
There are several different skeletal types.
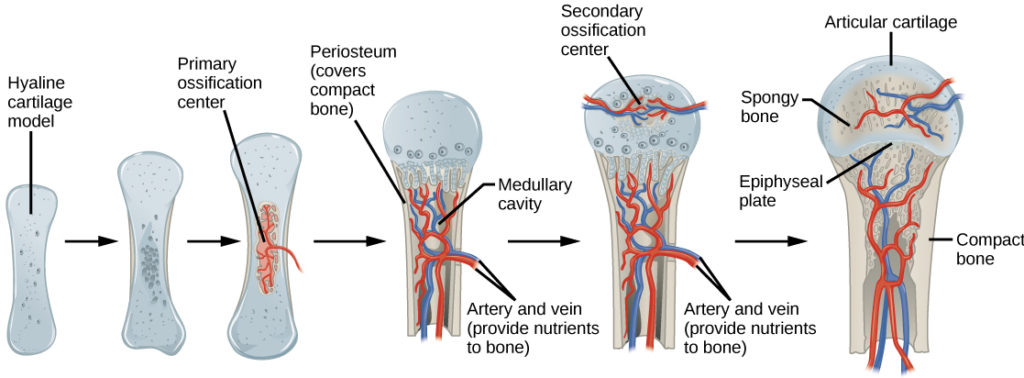
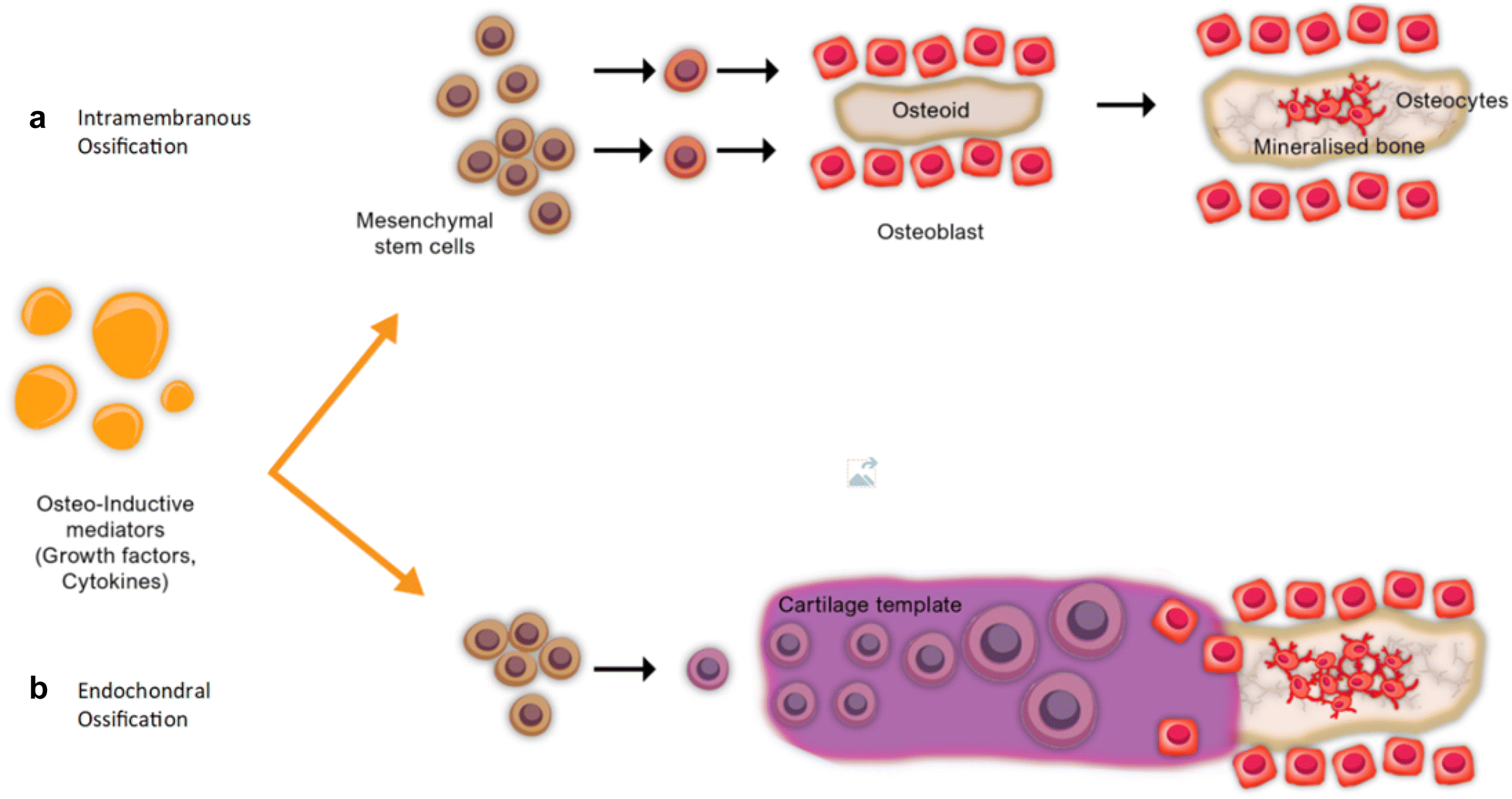
Osteoblast definition biology. Long bones follow the process of endochondral ossification where the diaphysis grows inside of cartilage from a primary ossification center until it forms most of the bone. Ossification begins as mesenchymal cells form a template of the future bone. Intramembranous ossification is complete by the end of the adolescent growth spurt while endochondral ossification lasts into young adulthood.
A normal bone ossification process can be of two different types. Cranial bone development starts in the early embryo from the neural crest and mesoderm cells. The skeleton refers to the frames of support of animal bodies.
Osteogenesis is a process by which new layers of bone tissues are laid by osteoblasts. Intramembranous ossification is the process of bone development from fibrous membranes. This develops in the epiphyses of bone during endochondral ossification.
Endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification. The apophysis is a site of tendon or ligament attachment as compared to the epiphysis which contributes to a joint. For land dwelling animals skeletons are also necessary to support movement since walking and flying rely on the ability to exert force on rigid levers such as legs and wings.
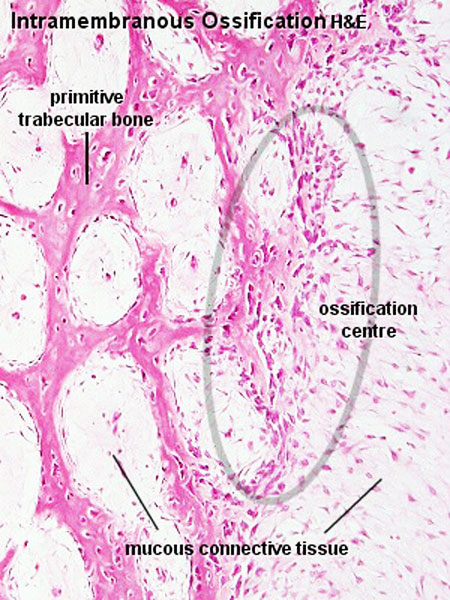
Some of these are paired bones. In longer bones is occurs at both ends in shorter bones it occurs in only one epiphysis. During intramembranous ossification fibrous connective tissue is replaced by bone.
The 8 cranial bones are the frontal parietal temporal occipital sphenoid and ethmoid bones. It is involved in the formation of the flat bones of the skull the mandible and the clavicles. In this anatomy course part of the anatomy specialization you will learn how the components of the integumentary system help protect our body epidermis dermis hair nails and glands and how the musculoskeletal system bones joints and skeletal muscles protects and allows the body to move.
A small band of hyaline cartilage remains in between the bones as a growth plate. What are cranial bones. Summary endochondral ossification vs intramembranous ossification.
The cranial bones develop by way of intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification. The skeleton is the supporting framework of an organismit is typically made out of hard rigid tissue that supports the form of the animals body and protects vulnerable organs. The apophysis is a normal secondary ossification center that is located in the non weight bearing part of the bone and eventually fuses with it over time most of the apophyses fuse during the 2 nd decade of life but this process can be delayed especially in female athletes.
More From Osteoblast Definition Biology
- Hinge Joint Connective Tissue
- Hinge Joint Grabcad
- Gliding Joint Picture
- Hinged Gear Joint
- Why Is The Nervous System Important For The Function Of All Body Systems
Incoming Search Terms:
- Fibrinolysis As A Target To Enhance Fracture Healing Nejm Why Is The Nervous System Important For The Function Of All Body Systems,
- Bone Development Human Anatomy And Physiology Lecture Notes Docsity Why Is The Nervous System Important For The Function Of All Body Systems,
- Schematic Representation Of Intramembranous And Endochondral Download Scientific Diagram Why Is The Nervous System Important For The Function Of All Body Systems,
- Chapter Two Line Title Here And Chapter Title Here And Here Why Is The Nervous System Important For The Function Of All Body Systems,
- Bone Development Intramembranous Ossification Tutorial Sophia Learning Why Is The Nervous System Important For The Function Of All Body Systems,
- Solved 9 Bones Develop In Two Ways Intramembranous Ossi Chegg Com Why Is The Nervous System Important For The Function Of All Body Systems,


:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/bone-tissue-formation/KNd677RWELj0dfjt2EPZvQ_sqdE9ExinfHoh3vlpNe3A_Endochondral_bone_formation.png)

