Medial Epicondyle Of Femur Pain, Lateral Epicondylitis Teachmesurgery
Medial epicondyle of femur pain Indeed lately has been hunted by users around us, maybe one of you personally. People are now accustomed to using the net in gadgets to view image and video data for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about Medial Epicondyle Of Femur Pain.
- Femur Bone Anatomy Proximal Distal And Shaft Kenhub
- Hip And Knee Pain Saylor Physical Therapy Cornelius
- Medial Knee Injuries Wikipedia
- Patellofemoral Joint Physiopedia
- Native Knee Kinematics Hip Knee Book
- Femur
Find, Read, And Discover Medial Epicondyle Of Femur Pain, Such Us:
- Medial Collateral Ligament Mcl Tears And Sprains
- Knee Anatomy Knee Joint Treatment Melbourne Knee Pain Treatment Melbourne
- Illitibial Band Syndrome Symptoms Treatment Tests
- Femur
- Unit Vii
If you re looking for Lateral Condyle Vs Epicondyle Fracture you've come to the ideal location. We have 104 graphics about lateral condyle vs epicondyle fracture adding images, photos, photographs, backgrounds, and more. In such web page, we additionally have number of graphics available. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, black and white, transparent, etc.

Evaluation Of Patients Presenting With Knee Pain Part Ii Differential Diagnosis American Family Physician Lateral Condyle Vs Epicondyle Fracture
The medial epicondyle is situated below and anterior to the adductor tubercle.
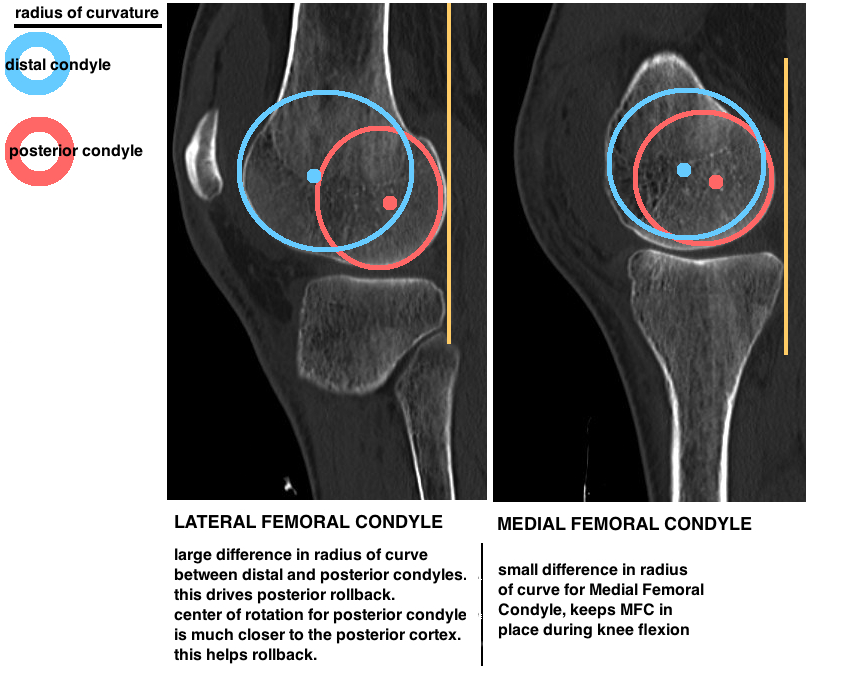
Lateral condyle vs epicondyle fracture. To identify patellar height you may evaluate the distance between the center of the patella and the palpable prominence of the medial femoral epicondyle. Below to the medial condyle of the tibia and medial surface of its body. During walking and running the iliotibial band is subjected to frictional and compressive forces over the lateral epicondyle.
Projecting from each condyle is an epicondyle that act as attachment sites for the collateral ligaments. Tibial stretches from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial tibial condyle. When approaching the knee joint the iliotibial tract passes the lateral epicondyle of the femur and splits into two structures.
The medial collateral ligament mcl aka. It also provides attachment for the tendon of adductor magnus muscle as well as the tibial collateral ligament supporting structure connecting the tibia to the femur. The iliopatellar band and a distal extension inserting at the gerdy tubercle figure 1.
It is attached proximally to the medial epicondyle of the femur immediately below the adductor tubercle. Prominent lateral and medial condyles are found at the distal end of the femur. The medial supracondylar line ends at the adductor tubercle where the adductor magnus attaches.
An anatomic descriptive study of 171 plain films of normal distal humeri of children aged 4 to 15 years demonstrated that the average location of the center of the intact medial epicondyle on ap radiographs is 05 mm below the olecranon fossa line and 12 mm anterior to the posterior humeral line in lateral radiographs. The knee joint is a hinge type synovial joint which mainly allows for flexion and extension and a small degree of medial and lateral rotation. A fracture of the medial epicondyle of the elbow that is the third most common fracture seen in children and is usually seen in boys between the age of 9 and 14.
It is formed by articulations between the patella femur and tibia. It resists forces that would push the knee medially which would otherwise produce valgus deformity. It is a broad flat membranous band situated slightly posterior on the medial side of the knee joint.
In this article we shall examine the anatomy of the knee joint its articulating surfaces ligaments and neurovascular supply. Furthermore the lateral epicondyle tends to have two prominent tubercles rather than one which makes the medial epicondyle a more reliable landmark for measurement.
More From Lateral Condyle Vs Epicondyle Fracture
- Glidingsliding Joint Examples
- Hinge Joint Similar
- What Tissue Connects Bone To Bone
- Hinge Joint Vocab
- What Connects Bone To Bone And Muscle To Bone
Incoming Search Terms:
- Giant Cell Tumour Sarcomatous Degeneration With Pathological Fracture Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org What Connects Bone To Bone And Muscle To Bone,
- Painful Plica Do They Exist Rayner Smale What Connects Bone To Bone And Muscle To Bone,
- Native Knee Kinematics Hip Knee Book What Connects Bone To Bone And Muscle To Bone,
- The Knee Joint Articulations Movements Injuries Teachmeanatomy What Connects Bone To Bone And Muscle To Bone,
- Unicondylar Fractures Of The Distal Femur Sciencedirect What Connects Bone To Bone And Muscle To Bone,
- Full Text Plica Syndrome And Its Embryological Origins Edorium Journal Of Orthopedics What Connects Bone To Bone And Muscle To Bone,






